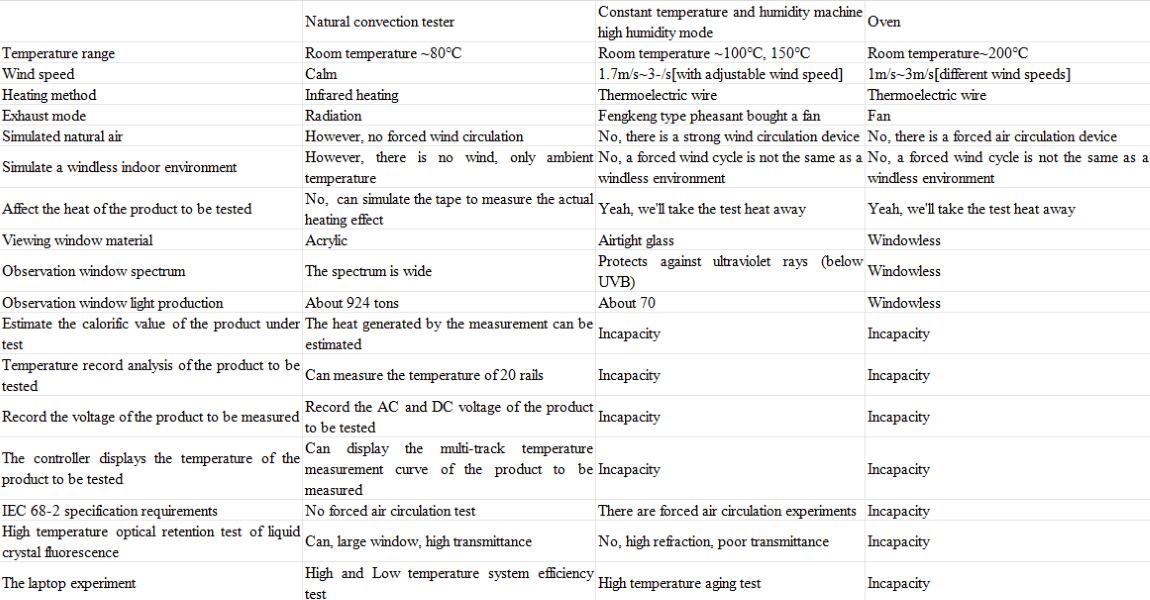
Comparison of Natural Convection Test Chamber, Constant Temperature and Humidity Test Chamber and High Temperature Oven
Instructions:
Home entertainment audio-visual equipment and automotive electronics are one of the key products of many manufacturers, and the product in the development process must simulate the adaptability of the product to temperature and electronic characteristics at different temperatures. However, when using a general oven or thermal and humidity chamber to simulate the temperature environment, either the oven or thermal and humidity chamber has a test area equipped with a circulating fan, so there will be wind speed problems in the test area.
During the test, the temperature uniformity is balanced by rotating the circulating fan. Although the temperature uniformity of the test area can be achieved through the wind circulation, the heat of the product to be tested will also be taken away by the circulating air, which will be significantly inconsistent with the actual product in the wind-free use environment (such as the living room, indoor).
Because of the relationship of wind circulation, the temperature difference of the product to be tested will be nearly 10℃. In order to simulate the actual use of environmental conditions, many people will misunderstand that only the test chamber can produce temperature (such as: oven, constant temperature humidity chamber) can carry out natural convection test. In fact, this is not the case. In the specification, there are special requirements for wind speed, and a test environment without wind speed is required. Through the natural convection test equipment and software, the temperature environment without passing through the fan (natural convection) is generated, and the test integration test is performed for the temperature detection of the product under test. This solution can be used for home related electronics or real-world ambient temperature testing in confined Spaces (e.g., large LCD TV, car cockpits, automotive electronics, laptops, desktops, game consoles, stereos, etc.).
Unforced air circulation test specification :IEC-68-2-2, GB2423.2, GB2423.2-89 3.31 The difference between the test environment with or without wind circulation and the test of products to be tested:
Instructions:
If the product to be tested is not energized, the product to be tested will not heat itself, its heat source only absorbs the air heat in the test furnace, and if the product to be tested is energized and heated, the wind circulation in the test furnace will take away the heat of the product to be tested. Every 1 meter increase in wind speed, its heat will be reduced by about 10%. Suppose to simulate the temperature characteristics of electronic products in an indoor environment without air conditioning. If an oven or a constant temperature humidifier is used to simulate 35 °C, although the environment can be controlled within 35 °C through electric heating and compressor, the wind circulation of the oven and the thermal and humidify test chamber will take away the heat of the product to be tested. So that the actual temperature of the product to be tested is lower than the temperature under the real windless state. It is necessary to use a natural convection test chamber without wind speed to effectively simulate the actual windless environment (indoor, no starting car cockpit, instrument chassis, outdoor waterproof chamber... Such environment).
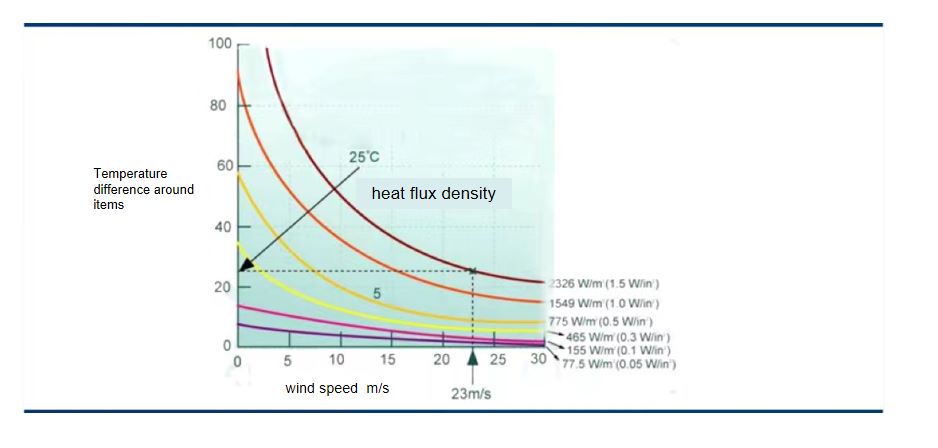
Comparison table of wind speed and IC product to be tested:
Description: When the ambient wind speed is faster, the IC surface temperature will also take away the IC surface heat due to the wind cycle, resulting in the faster the wind speed and the lower the temperature.